The 4Cs of Diamond Grading Guide
The four characteristics: cut, carat (weight), clarity, and color determine how much a diamond is worth.
Diamond proportion is very important. Round brilliant diamonds are usually cut with 58 facets. The proportionional similarity of these facets on the diamond affect how much light will be reflected to the viewer. The better the cut, the more the diamond will sparkle. Ask for the table percentage. A good table percentage is between 55-60%.
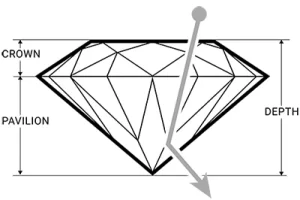
How does pavilion depth affect a diamond’s cut?
Precise artistry and workmanship are required to fashion a stone so its proportions, symmetry and polish deliver the magnificent return of light only possible in a diamond.
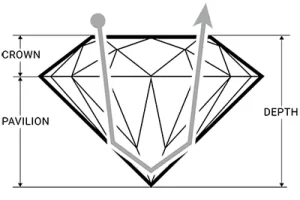
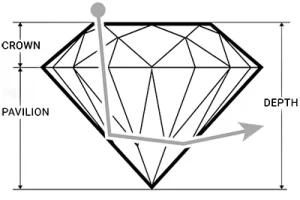
A pavilion depth that’s too shallow or too deep will allow light to escape from the side of the stone or leak out of the bottom. A well-cut diamond will direct more light through the crown, creating maximum brilliance.
TOO SHALLOW |
IDEAL |
TOO DEEP |
Cut also determines the shape such as pear, round or oval. When having a diamond mounted, appraise and record the stone’s measurements which never change. After the stone is mounted, verify that it matches the measurements and/or appraisal certificate.
ROUND |
PRINCESS |
TRILLIANT |
BAGUETTE |
EMERALD |
MARQUISE |
PEAR |
HEART |
OVAL |
CUSHION |
ASSCHER |
RADIANT |
Carat is the measurement of a gem’s weight. Larger gems often cost more per carat because of their size. There are 100 points to a carat. A 50 point diamond equals 1/2 a carat. One gram is 5 carats. Ascertain the actual point size of a diamond instead of the fractional weight. Some jewelers will try to sell a .90 diamond as a 1 carat diamond which would be much more expensive.
 0.25 Carat 4.1 mm 0.25 Carat 4.1 mm |  0.50 Carat 5.0 mm 0.50 Carat 5.0 mm |  0.75 Carat 5.8 mm 0.75 Carat 5.8 mm |  1.00 Carat 6.5 mm 1.00 Carat 6.5 mm |  1.50 Carat 7.4 mm 1.50 Carat 7.4 mm |  2.00 Carat 8.2 mm 2.00 Carat 8.2 mm |
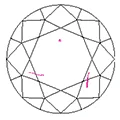
Clarity or clearness ranges from flawless (perfect) to I (included):
- Flawless: perfect inside and out.
- Internally Flawless: might have minor blemishes on the outside.
- VVS1, VVS2: have very tiny inclusions.
- VVS1 inclusions are only visible through the pavilion.
- VVS2 inclusions are slightly larger.
- VS1, VS2: have very small inclusions.
- VS1 inclusions are smaller than VS2 and harder to detect.
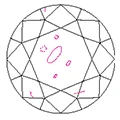
- SI1, SI2, SI3: have small inclusions.
- I1, I2, I3: have inclusions that can be seen by the naked eye.
VVS2 |
VS2 |
SI2 |
I2 |
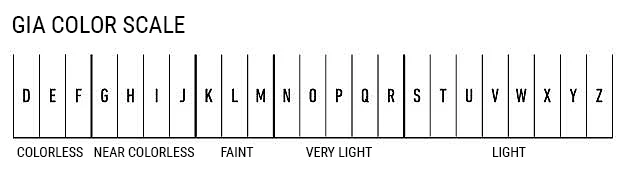
Colors range from D – X for white and yellow diamonds. D is the whitest. At S they are “Fancy” yellow Diamonds. There are also, pink, red, green, blue and brown diamonds which are typically irradiated.

What Is Diamond Grading?
Diamond grading is the professional process of evaluating a diamond’s physical and visual characteristics. Certified gemologists examine each diamond under controlled conditions to determine its quality based on standardized criteria.
A diamond grading report allows buyers to objectively compare diamonds and ensures transparency before purchase. Every diamond is unique, and grading helps identify the true value and appearance of each stone.
Diamond Grading Glossary
Brilliance: The intensity of white light reflected through the top of the diamond, making it sparkle.
Crown: The top portion of a diamond, extending from the girdle up to the table.
Culet: The small facet at the tip of the bottom of the diamond.
Depth: The total height of a gemstone, measured from the culet to the table.
Diameter: The width of the diamond across the girdle, often used to estimate size.
Dispersion: When white light splits into rainbow colors inside the diamond.
Eye Clean: A diamond with no visible flaws to the unaided eye from about 12 inches, face up.
Face Up: Viewing the diamond from the top, the standard perspective for evaluating sparkle.
Facet: Flat, polished surfaces on the diamond; most diamonds have 57 facets.
Fire: Flashes of color reflected from inside the diamond due to dispersion, like a prism effect.
Flaw: Any internal or external imperfection in a diamond.
Fluorescence: Glow a diamond shows under ultraviolet light; commonly blue but can vary.
Girdle: The narrow band around the widest part of the diamond; can be faceted or smooth.
Inclusion: Impurities inside a diamond; fewer inclusions give higher clarity.
Pavilion: The bottom part of a diamond, from below the girdle to the culet.
Polish: Smooth, shiny finish on facets; ideal polish maximizes brilliance.
Proportions: Measurement of cut quality including depth, table, crown, pavilion, and symmetry, affecting light reflection.
Scintillation: Sparkle seen as flashes of light when a diamond moves.
Symmetry: How uniformly facets align; better symmetry produces more sparkle.
Table: The largest flat facet on top of a diamond.
Diamond Certification and Why It Matters
A diamond grading certificate is your key to buying with confidence. It confirms the quality and authenticity of a diamond, providing a detailed report from trusted laboratories that explains the 4Cs — cut, color, clarity, and carat — along with other important characteristics. Whenever you’re investing in high-value jewelry, always request a grading report. Certification ensures transparency, protects your purchase, and gives you peace of mind knowing exactly what you’re getting.
When choosing the right diamond, start with the cut, as it determines the sparkle and overall visual impact. Next, balance color and clarity: diamonds in the G–H color range with eye-clean clarity offer excellent value without compromising beauty. Carat weight is important, but bigger is not always better — it’s the combination of cut, color, and clarity that makes a diamond truly stunning.
Caring for Diamond Jewelry
Diamonds are durable but require proper care:
- Store separately: Prevent scratches by keeping diamonds apart.
- Clean regularly: Use mild soap and a soft brush. Avoid harsh chemicals.
- Avoid impacts: Remove jewelry during heavy work or sports.
- Inspect settings: Check prongs and mountings annually with a jeweler.
Even durable diamonds can chip if hit hard. Chlorine bleach can discolor or weaken the setting. A professional jeweler’s yearly inspection maintains shine, prevents damage, and ensures your diamond stays secure.
Proper care maintains brilliance and protects long-term value.
Why Certification Affects Diamond Value
Certified diamonds have higher resale value, easier insurance coverage, and stronger buyer confidence compared to uncertified stones.
Final Thoughts
Understanding diamond grading empowers you to choose jewelry that reflects beauty, quality, and meaning. At Diamonds n Colors, we believe knowledge enhances confidence and ensures every diamond tells a story worth cherishing.
Tips for General Care
Even though you may wear your diamond ring 24 hours a day, you should still give thought to its care.
- Don’t wear it when you’re doing rough work.
- Even though a diamond is durable, it can be chipped by a hard blow.
- Don’t let your diamond come in contact with a chlorine bleach when you’re doing household chores.
- It can damage and discolor the mounting.
Do see your jeweler at least once a year and have him check your ring and other precious pieces for loose prongs and wear of mountings. He’ll usually give them a professional “shine-up” too.
What Our Clients Are Saying
At DiamondNColors, we take pride in delivering exceptional service and exquisite jewelry. From diamond rings, engagement rings, and bracelets to gemstone pieces and more, our clients’ experiences speak for themselves. Explore our genuine testimonials to see how we bring elegance and quality to every piece, and share your own feedback here.
FAQs
Diamond grading guide is the professional evaluation of a diamond’s cut, color, clarity, and carat weight. It is important because grading helps buyers understand diamond quality, compare stones fairly, and make confident purchasing decisions based on certified standards.
The 4Cs of diamond grading guide are cut, color, clarity, and carat. These factors determine a diamond’s sparkle, appearance, rarity, and value, helping buyers balance beauty and budget when selecting diamonds for engagement rings or fine jewelry.
The best diamond grading guide cut for maximum sparkle is an Excellent or Very Good cut. A well-cut diamond reflects light efficiently, producing brilliance and fire, while poorly cut diamonds can appear dull even with high color or clarity grades.
Diamond color grading measures how colorless a diamond appears. Near-colorless diamonds, such as G or H grades, often look white to the naked eye and offer excellent value, while higher grades are rarer and more expensive.
Yes, diamond certification is essential because it provides an unbiased evaluation of a diamond’s quality. A grading report from a trusted laboratory confirms the 4Cs, ensures transparency, and protects buyers when purchasing high-value diamond jewelry.